Views
| Line 434: | Line 434: | ||
| - | + | == Publication == | |
Revision as of 02:39, 17 May 2010
Contents |
Goal
- To understand how the mind, behavior and brain are interrelated by linking key cognitive & emotional functions to neural activities at multiple levels of brain systems.

Plans
The Strategy of Linking Brain and Mind (SLBM)
First, we have identified a set of comprehensive but focused set of cognitive functions and targeted brain mechanisms with an aim to achieve breadth while insuring that our studies fall squarely within the areas of expertise of our associated faculty (Fig 1A, 1B). Second, to address the 'linking' questions around those key cognitive and brain mechanisms, we intend to integrate cutting-edge ‘neurometric' techniques to probe neural activities/structures at multiple levels spanning the depth of genetic, molecular, synaptic, neuronal, local/global network-level measurements (Fig 1C). These brain measurements will be paralleled by state-of-the-art 'psychometric' tools to capture mind in action, with behavioral tasks spanning the breadth of behavioral genetics, rodent memory tasks, visual perception tasks, eye movements, reverse correlation and social perception tasks (Fig 1D). Third, based on the neurometric and psychometric data, we will build tight linkages between brain activity/structure and mind. In doing so, computational approaches will help us to build comprehensive neural models constrained by data from empirical studies (Fig 1E). Computational models of complex brain systems allow us to put to test, via simulation, predictions that cannot be tested in empirical situations and to guide empirical studies by generating testable predictions about behaviors in the domains of both brain and mind. In addition, we will study brains and minds in abnormal states by specifying the roles of neural circuits underlying cognitive deficits in patients with psychiatric disorders and in individuals with remarkable cognitive abilities that fall outside the range of normal (Fig 1F). Our multi-level approach, transpiring through 'gene', 'protein', 'neuron', 'system', 'behavior', 'abnormality' and 'computation', can lead to fundamental cure for mental diseases in the future.
step 1 Identification of key Cognitive & Brain mechanisms
|
Perirhinal cortex / Entorhinal cortex / Parietal cortex / Hippocampus / Amygdala / Visual cortex / Prefrontal cortex / Corpus callosum / Orbitofrontal cortex / Longrange cortical circuitry |
|
step 2 Integration of key Neurometric & Psychometric tools

step 3 Linking Neural Activities to Cognitive Functions
Research Units
Three Core Research Units
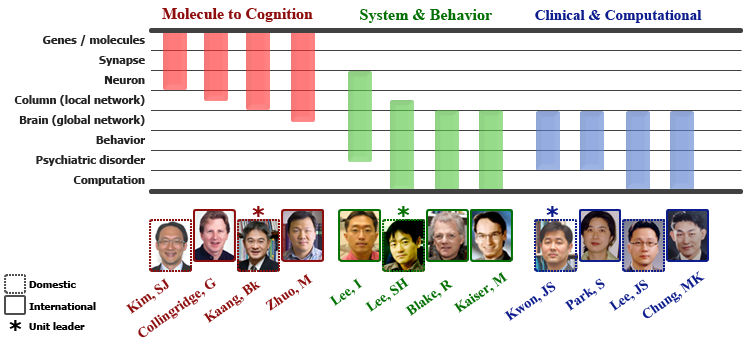
Research overview
| I. Introduction and overview of research plans Our research aim is to use biological, behavioral and computational methods to understand how the mind, brain and behavior are interrelated. Studying humans and animals, our research will link key cognitive and emotional functions to neural activities at multiple levels of brain systems. To establish these linkages, we set forth a research strategy, named 'SLBM (Strategy of Linking Brain and Mind)', the major steps and components of which are summarized in the following three sections.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||












